Conformer Generation for Structure-Based Drug Design: How Many and How Good?
Andrew T. McNutt, Fatimah Bisiriyu, Sophia Song, Ananya Vyas, Geoffrey R. Hutchison, and David Ryan Koes. “Conformer Generation for Structure-Based Drug Design: How Many and How Good?” J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63(21) 6598–6607 Online
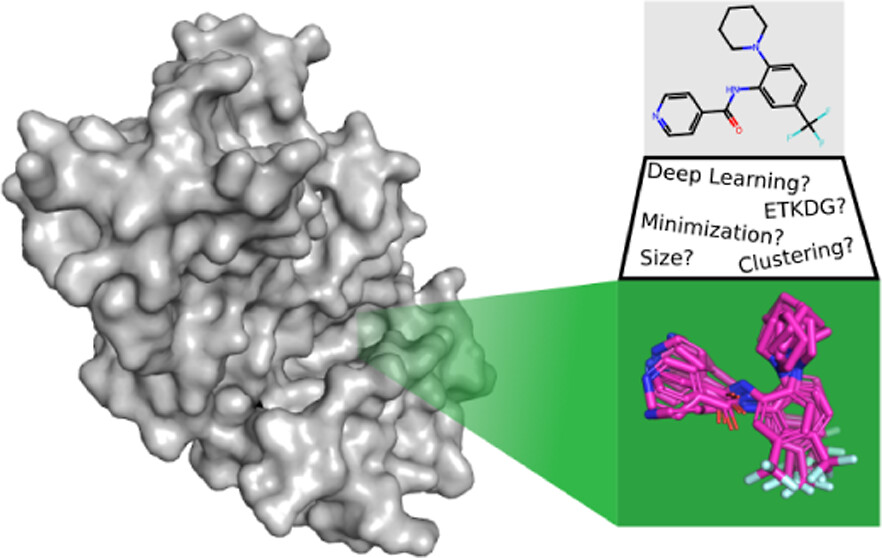 Conformer generation, the assignment of realistic 3D coordinates to a small molecule, is fundamental to structure-based drug design. Conformational ensembles are required for rigid-body matching algorithms, such as shape-based or pharmacophore approaches, and even methods that treat the ligand flexibly, such as docking, are dependent on the quality of the provided conformations due to not sampling all degrees of freedom (e.g., only sampling torsions). Here, we empirically elucidate some general principles about the size, diversity, and quality of the conformational ensembles needed to get the best performance in common structure-based drug discovery tasks. In many cases, our findings may parallel “common knowledge” well-known to practitioners of the field. Nonetheless, we feel that it is valuable to quantify these conformational effects while reproducing and expanding upon previous studies. Specifically, we investigate the performance of a state-of-the-art generative deep learning approach versus a more classical geometry-based approach, the effect of energy minimization as a postprocessing step, the effect of ensemble size (maximum number of conformers), and construction (filtering by root-mean-square deviation for diversity) and how these choices influence the ability to recapitulate bioactive conformations and perform pharmacophore screening and molecular docking.
Conformer generation, the assignment of realistic 3D coordinates to a small molecule, is fundamental to structure-based drug design. Conformational ensembles are required for rigid-body matching algorithms, such as shape-based or pharmacophore approaches, and even methods that treat the ligand flexibly, such as docking, are dependent on the quality of the provided conformations due to not sampling all degrees of freedom (e.g., only sampling torsions). Here, we empirically elucidate some general principles about the size, diversity, and quality of the conformational ensembles needed to get the best performance in common structure-based drug discovery tasks. In many cases, our findings may parallel “common knowledge” well-known to practitioners of the field. Nonetheless, we feel that it is valuable to quantify these conformational effects while reproducing and expanding upon previous studies. Specifically, we investigate the performance of a state-of-the-art generative deep learning approach versus a more classical geometry-based approach, the effect of energy minimization as a postprocessing step, the effect of ensemble size (maximum number of conformers), and construction (filtering by root-mean-square deviation for diversity) and how these choices influence the ability to recapitulate bioactive conformations and perform pharmacophore screening and molecular docking.